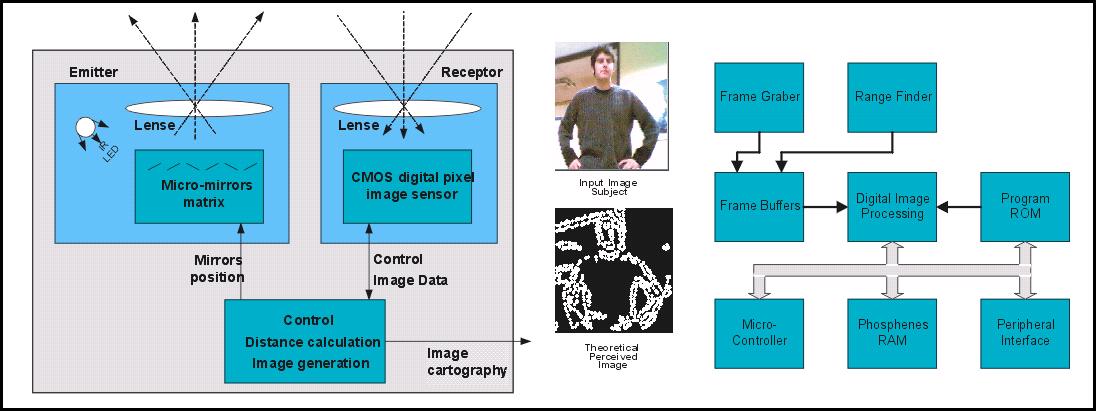
Since the stimulation cannot result in a high quality image, some modifications of the acquired image have to be done for the patient to help understand what he sees. Enhancements are performed by processing the captured image and 3D information of this image is calculated by a range finder system.
Image acquisition is done by a CMOS image sensor constituted of an array of digital pixel sensors. The 3D information of the image is calculated by a range finder system, which emits a pattern of infrared light via a micro-mirrors array, to sense it by an image sensor. The distance calculation, based on triangulation principles, can then be performed.
Images of the outside world have to be represented as phosphenes patterns (bright spots in the subject’s vision field). The 3 basic processing steps are:
– preprocessing (e.g. Histogram equalization);
– processing (e.g. Segmentation, thresholding);
– pitting to phosphene map.
Different effects are available, depending on situation : reading, inside/outside displacement, etc.